Military Surveillance Drone: ISR and Autonomous Operations
The drone industry is expanding rapidly, particularly due to the growing demand for advanced military surveillance drones. These drones are essential for national defense and maintaining national security.
Military surveillance capabilities enable armed forces to assess threats and ensure public safety.
According to The Guardian, the United States alone is expected to procure approximately 43,000 lightweight surveillance drones by 2028—more than the rest of the world combined. This massive procurement highlights the global shift away from traditional manned reconnaissance toward flexible, remote aerial intelligence. As these military drones evolve, concerns about autonomy, connectivity, and cybersecurity are coming to the forefront.
This guide offers an in-depth exploration of military surveillance drones, covering their features, practical applications, and future prospects. Learn more about how UAV technology is redefining the modern battlefield.
Table of Contents
Enhancing Military Surveillance: the Role of Defense Drones
Definition and Basics
Defense drones, also known as combat drones or military UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), are used by military forces for surveillance and conflict prevention. These remotely piloted aircraft are invaluable force multipliers in various operational domains, ranging from peacekeeping to high-intensity conflict zones. They can be divided into two main categories based on range, navigation methods, and weight.
- Tactical drones: They typically weigh between 16 grams and 150 kilograms, have a line-of-sight range of up to 200 kilometers, and can reach altitudes of 10,000 feet. They are generally designed for rapid localized intelligence gathering
- Strategic drones: They weigh more than 150 kilograms and offer long-endurance capabilities. These larger platforms often carry sophisticated sensor packages and can cover hundreds of kilometers in a single mission.
Military surveillance drones are suitable for a wide range of uses, including:
- Border patrol
- Search and rescue
- Law enforcement support
- Special operations
- Force protection
- Target acquisition
In addition, both categories of drones can be armed as needed. Advanced designs, such as VTOL Fixed Wing technology, further extend their long-range capabilities in hostile environments.
Pros and Cons of Defense Drones
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Rapid deployment, response, and reactivity. | Weather resistance sensitivity (especially to wind and rain, which can compromise flight time stability). |
| Payload flexibility: multi-sensors including EO/IR, Laser RangeFinder (LRF), Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), Ground Moving Target Indicator (GMTI), and communication relays for extended C2 (Command and Control). | Cybersecurity risks (addressed by encrypted communications). The threat of hacking necessitates military-grade anti-jamming measures. |
| Long endurance for tethered drones (up to 50 hours) providing persistent aerial monitoring. | Limited flight time autonomy (current battery technology constraints result in a few minutes to 4–5 hours for free drones). |
| Increased security for ground units with unmanned aircraft systems. | Reduced range capacity for smaller drones. |
| Cost-efficient technology in terms of acquisition, maintenance, and ROI compared to traditional manned aircraft. | Need for military-grade durability and IP rating for extreme environments ensures operability in dust, rain, and extreme temperatures. |
Leveraging Tactical Drone Technology to Maximize Military Operations
Tactical Drones: Defining autonomous intelligence
Designed specifically for military applications, tactical defense drones, also known as tactical unmanned aerial vehicles (TUAVs), feature versatile Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) capabilities.
Their primary mission is to support ground forces gathering information through real-time observation, interception, and jamming. They provide commanders with immediate enhanced situational awareness.
- Rapid deployment: Their small logistics footprint ensures swift deployment.
- Operator efficiency: They can often be operated by a single land force member.
- Adaptability: Modular payloads enhance flexibility across diverse operational demands.
Note that the autonomy and analysis capabilities of these drones depend on their specific functionalities.
Tactical Drone’s added Value: Strengthening ISR/ISTAR Missions
Tactical drones are highly effective for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) or even Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance (ISTAR) operations.
An key component of these military surveillance drones is the Variable Height Antenna (VHA), which is positioned at around 100 meters. The VHA acts as a relay, amplifying the wave propagation to achieve multiple objectives:
- Extending the Line of Sight (LOS) and improving operator visibility
- Overcoming obstacles in challenging terrain, such as dense forests or mountains, to ensure uninterrupted high-speed communication and real-time aerial support
These military surveillance drones have remote detection capabilities, enabling laser telemetry for accurate target distance assessment. With infrared cameras and optical zoom capabilities, the drones excel in both day and night conditions. Their ability to gather multi-spectral data provides a comprehensive picture, which is critical for distinguishing targets from environmental clutter.
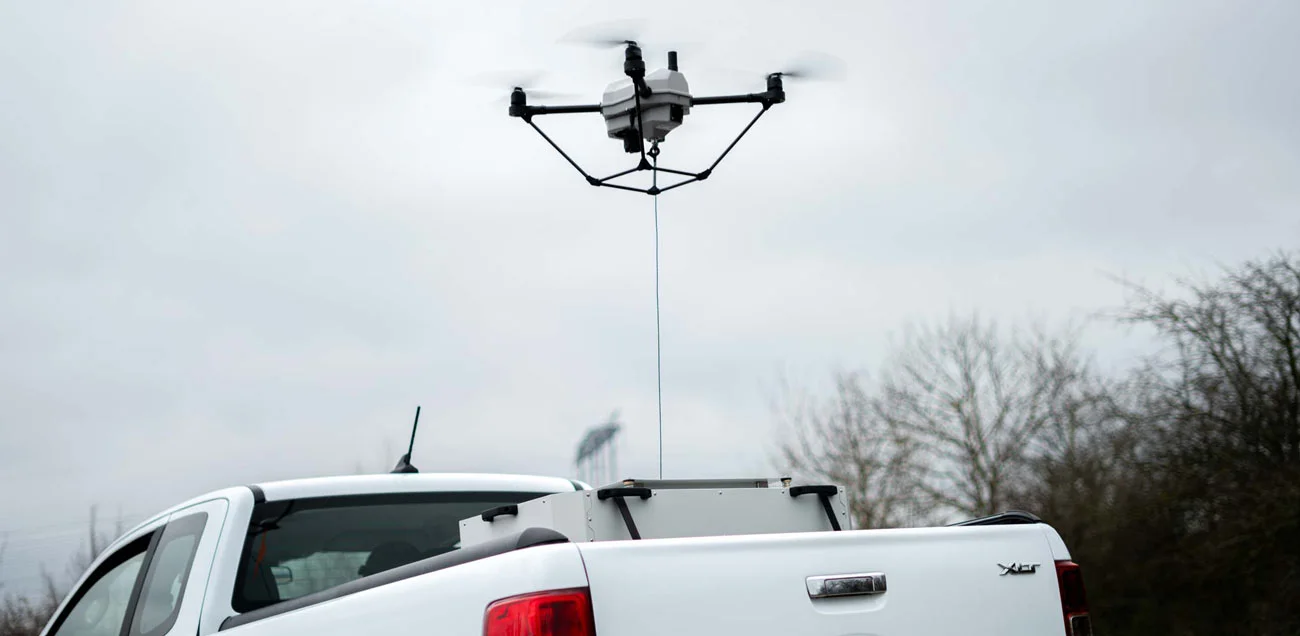
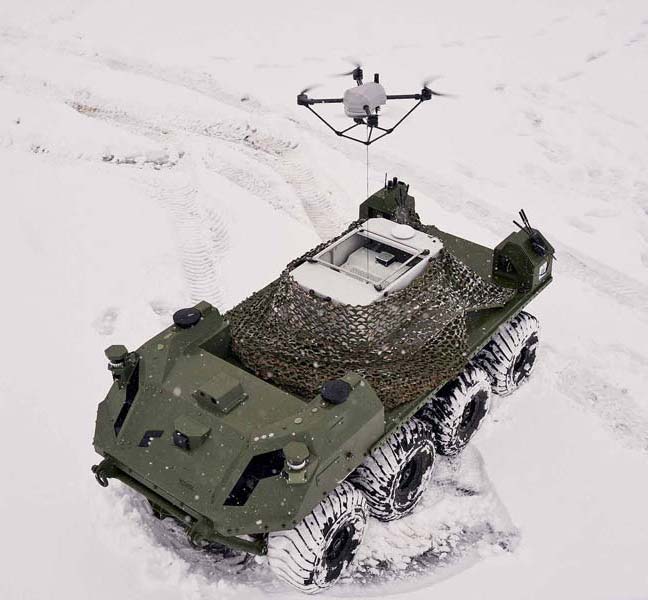
Tethered Drones: The ultimate stealth and endurance solution
For individuals or organizations requiring the utmost discretion, tethered tactical drones are superior to radio-controlled ones. These types of military surveillance drones have the distinct advantage of operating without generating detectable waves, ensuring a higher level of stealth and secrecy during operations.
Furthermore, their connection to a ground station via cables provides continuous power, enabling long-duration missions of up to an impressive 50 hours—ideal for persistent surveillance.
Companies like Elistair have perfected the tethering station, automating launch and recovery, and guaranteeing near-uninterrupted aerial oversight
AI-Driven Surveillance and Border Patrol Operations
Border Patrol Drones in a Nutshell
The use of military surveillance drones has risen sharply over the past decade, expanding beyond first responders to include a range of units such as armies, border police, and customs.
The primary goal of border patrol drones is to monitor and secure critical areas such as borders and hostile environments (both on land and at sea), and to facilitate search and rescue operations.
- Deterrence: The presence of these drones proactively deters illicit activities, including smuggling, drug trafficking, and unauthorized population movements.
- Cost-effectiveness: They are a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to manned aircraft for covering large patrol areas, avoiding the high operational costs associated with jets or helicopters.
Technological Advantages: Autonomous Patrols and AI
Military surveillance drones are at the forefront of technological innovation, equipped with advanced sensors and cameras (for functions such as obstacle avoidance) and high-resolution imaging,
Their integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) allows them to provide real-time data to authorities and law enforcement agencies. This capability allows them to:
- Respond quickly and efficiently to potential threats, even in low-light conditions.
- Perform autonomous patrols and return to docking stations for continuous coverage.
- Execute object tracking and anomaly detection without constant human oversight.
Understanding Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR)
ISR vs. ISTAR: Roles and Distinctions in Military Operations
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) are essential components of military operations.
● Intelligence: The end product of ISR, Intelligence relates to the collection, analysis, and interpretation of information for informed decision making and strategic advantage.
● Surveillance: It refers to the continuous observation of enemy activity or specific targets in the battlespace.
● Reconnaissance: It involves the gathering of information to address specific military objectives and inquiries. This often requires penetrating deeper into enemy territory or challenging terrain.
ISTAR encompasses Target Acquisition, which provides critical information to neutralize, destroy, or stop threats, and includes aspects of situational awareness not explicitly covered by ISR.
Cyber-Resilience and The Future of Defense Drone Technology
Military surveillance drones, whether tactical or strategic UAVs, have revolutionized battlefield operations by enhancing the security of ground units through constant aerial support and enabling discreet intelligence gathering.
However, challenges such as adverse weather conditions, limited range, and the quest for greater autonomy require innovative solutions.
The industry is currently focusing on:
- Implementing encrypted communications and anti-jamming measures to mitigate hacking and cyber risks.
- Developing counter-UAS (Counter-Unmanned Aircraft Systems) capabilities, in which the drones themselves can assist in neutralizing adversarial drone threats.
Continued advancement in AI, battery endurance, and modular payload design will further solidify the indispensable role of drone technology in military and law enforcement operations.
The future of the defense sector relies heavily on these unmanned combat systems to provide superior endurance and global, real-time intelligence gathering capabilities.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Military Surveillance Drones
What is the primary role of Military Surveillance Drones (UAVs) and why is their use growing rapidly?
Their main role is to enhance Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities for armed forces, national security, and border patrol. Their use is increasing because they offer a flexible, cost-effective, and remote solution for intelligence gathering, minimizing risk to ground units compared to traditional manned aircraft.
What is the key distinction between Tactical Drones and Strategic Drones?
Drones are primarily categorized by weight and range. Tactical Drones are lighter (16g to 150kg), have a shorter range (up to 200km Line of Sight), and are designed for rapid, localized intelligence gathering. Strategic Drones are heavier (over 150kg) and offer long-endurance capabilities to cover hundreds of kilometers in a single mission.
What are the key advantages of tethered tactical drones?
Tethered drones are connected to a ground station via a cable, which provides them with a continuous power supply. This enables long-duration missions of up to 50 hours for persistent surveillance. Furthermore, they operate without generating detectable waves, ensuring a high level of stealth and secrecy during operations.
How are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advanced technology enhancing these drones?
AI enables the drones to perform autonomous patrols, anomaly detection, and object tracking without constant human oversight. Combined with sophisticated sensors (EO/IR, LRF, SAR, GMTI), this capability provides authorities with real-time data for quick and efficient threat response, even in low-light conditions.
What are the main challenges facing the future of military drone technology?
Key challenges include:
- sensitivity to adverse weather,
- limited battery autonomy for untethered drones,
- cybersecurity risks (hacking and jamming).
The industry is focusing on enhancing durability, implementing encrypted communications and anti-jamming measures, and developing Counter-UAS (C-UAS) capabilities to neutralize adversarial drones.