Decoding Military Surveillance Drones: The Ultimate Guide
The drone industry is rapidly expanding, driven particularly by the increasing demand for advanced military drones, as it is crucial for national defense. Indeed, military surveillance enables armed forces to assess threats and ensure national security.
According to The Guardian, by 2028, the United States alone is expected to procure more lightweight surveillance drones (approximately 43,000) than the rest of the world combined. As military surveillance drones evolve rapidly, concerns about autonomy, connectivity, and cybersecurity come to the forefront. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of military surveillance drones, covering their features, practical applications, and future prospects. Read on to learn more.
Table of Contents
Enhancing Military Surveillance: the Role of Defense Drones
Definition and Basics
Defense drones, also known as combat drones, are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) used by military forces for surveillance and conflict prevention. They can be divided into two categories based on range, navigation methods, and weight:
1. Tactical drones: Weigh between 16 grams and 150 kilograms (with a line of sight of up to 200 kilometers and can reach altitudes of 10,000 feet)
2. Strategic drones: Weigh more than 150 kilograms
Military surveillance drones are suitable for a wide range of uses, including border patrol, search and rescue, law enforcement support and special operations in environments ranging from non-hostile to hostile. In addition, both categories of drones can be armed as required.
Pros and Cons of Defense Drones
Advantages
- Rapid deployment/reactivity
- Payload: Multi-sensors including EO/IR, Laser RangeFinder (LSF), synthetic aperture radar (SAR), ground moving target indicator (GMTI), and communication relays
- Long endurance for tethered drones (up to 50 hours)
- Increased safety for ground units with unmanned aircraft systems
- Cost-efficient technology in terms of acquisition, maintenance, and ROI
Common Challenges
- Weather sensitivity
- Hacking (mainly available on free drones)
- Limited flight autonomy (a few minutes to 4-5 hours for free drones)
- Reduced range capacity for smaller drones
Leveraging Tactical Drone Technology to Maximize Military Operations
Tactical Drones: What are they and how can they be used?
Designed specifically for military applications, tactical defense drones, also known as tactical unmanned aerial vehicles (TUAVs), feature versatile vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capabilities.
Their primary mission? To help ground forces gather information through real-time observation, interception and jamming.
It’s worth noting that the autonomy and analysis capabilities of these drones can vary depending on their specific functionalities.
Tactical Drone’s added Value: Strengthening ISR Missions
Tactical drones are highly effective for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) or even Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance (ISTAR) operations.
An integral part of this type of military surveillance drone is the Variable Height Antenna (VHA), which is positioned at approximately 100 meters. The VHA acts as a relay, amplifying the wave propagation to achieve multiple objectives:
- Extending line of sight (LOS) and improving operator visibility
- Overcoming obstacles in challenging terrain, such as dense forests or mountains, to ensure uninterrupted high-speed communication and real-time aerial support
These military surveillance drones have remote detection capabilities, enabling laser telemetry for accurate target distance assessment. In addition, they can carry variable electromagnetic payloads to detect telecommunications activity. With infrared cameras and optical zoom capabilities, they excel in both day and night conditions.
Thanks to their compact size and weight, tactical drones are affordable and can:
- Perform medium to long-duration missions
- Carry multiple sensors
- Ensure rapid deployment due to their small logistic footprint
- Be operated by one member of the land force
For individuals or organizations requiring the utmost discretion, tethered tactical drones are superior to their radio-controlled counterparts. These types of military surveillance drones offer a distinct advantage in that they operate without generating detectable waves, ensuring a higher level of stealth and secrecy during operations.
Border Patrol Drones: Beyond Search and Rescue Operations
Border Patrol Drones in a Nutshell
The use of military surveillance drones has risen sharply over the past decade, extending beyond first responders to a wide range of units, including armies, border police, and customs.
The primary goal of border patrol drones is to monitor and secure critical areas such as borders and hostile environments, both on land and at sea, and to facilitate search and rescue operations.
When used in rescue missions, surveillance drones provide real-time aerial imagery of areas that are inaccessible or dangerous to human responders. They help to locate survivors, assess the extent of damage, and guide rescue teams, facilitating timely and effective rescue operations.
Patrol drones are also ideal for border surveillance because they can be deployed quickly and conveniently. And with remote control capabilities, operators can effortlessly maneuver these surveillance drones from a secure location.
Technological and Environmental Advantages
Equipped with advanced sensors and cameras (for functions such as obstacle avoidance) and high-resolution imaging, military surveillance drones are at the forefront of technological innovation.
Their integration with AI allows them to provide real-time data to authorities and law enforcement agencies. This capability allows them to respond quickly and efficiently to potential threats, even in low-light conditions, thereby enhancing overall security measures.
In addition to their surveillance capabilities, the presence of these drones acts as a proactive deterrent to a wide range of illicit activities, including but not limited to smuggling, drug trafficking, and large-scale population movements. Thereby, they contribute to the maintenance of law and order in various environments.
Patrol drones are also a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to manned aircraft. Their ability to cover large areas and monitor remote locations makes them an indispensable tool for maintaining vigilance and protecting against security breaches.
What is Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR)?
ISR vs. ISTAR: Understanding their Roles and Distinctions in Military Operations
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) are essential components of military operations. Here’s a look at what each entails.
● Intelligence: As the end product of ISR, it relates to the collection, analysis, and interpretation of information for informed decision making and strategic advantage. It is also enriched by sources like human intelligence (HUMINT), signal intelligence (SIGINT), and satellites.
● Surveillance: Refers to the continuous observation of enemy activity or specific targets in the battlespace.
● Reconnaissance: Involves the gathering of information to address specific military objectives and inquiries.
The difference between ISR and ISTAR
Unlike ISR, ISTAR encompasses the action of target acquisition and provides critical target information to neutralize, destroy, or stop threats.
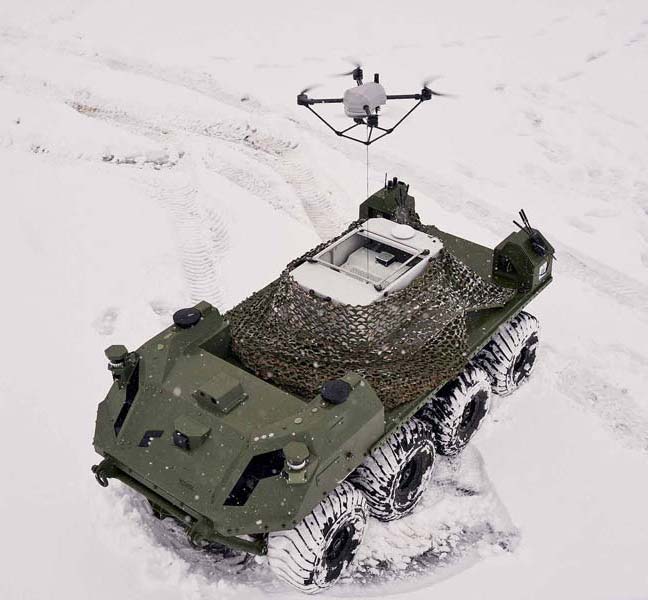
ISR and Tethered Drones: a Winning Combo?
The versatility of tethered drones makes them indispensable tools in ISR operations. They provide critical support for a range of intelligence missions, from observation to SIGINT.
Equipped with advanced imaging and radio technologies, these military surveillance drones provide a comprehensive, real-time understanding of military environments. They enhanced situational awareness by intercepting communications, monitoring movement and facilitating strategic resource allocation.
Linked to ground stations via cables, tethered drones remain operational for extended periods of time, enduring missions of up to an impressive 50 hours. Their autonomy and ability to gather intelligence in non-visual areas have made them invaluable assets in military operations.
Military surveillance drones, whether tactical or strategic UAVs, have revolutionized battlefield operations by enhancing the security of ground units through constant aerial support and enabling discreet intelligence gathering.
Drone technology is quickly becoming a fundamental tool for military and law enforcement agencies. However, as with any advancement, there are obstacles to overcome. Challenges such as adverse weather conditions, limited range, and the quest for greater autonomy require innovative solutions that, when achieved, will further cement drone technology’s position as an indispensable asset in military and law enforcement operations.