What Are The Benefits Of Tethered Drones?
Russel A
5 minutes
The market for tethered drones is growing exponentially as more commercial industries adopt them for their operations. Advanced technological developments in tethered UAVs have opened up new possibilities for surveillance aérienne, border patrol, setting up temporary communication towers and much more.
What Are Tethered Drones?
Adoption of the tethered drones technology in the commercial sector recently began in 2016. Today, many defense analysts consider the technology as an integral part of future bases.
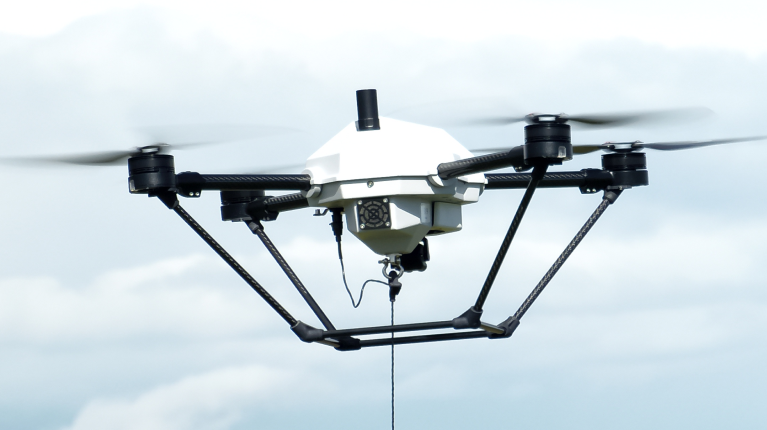
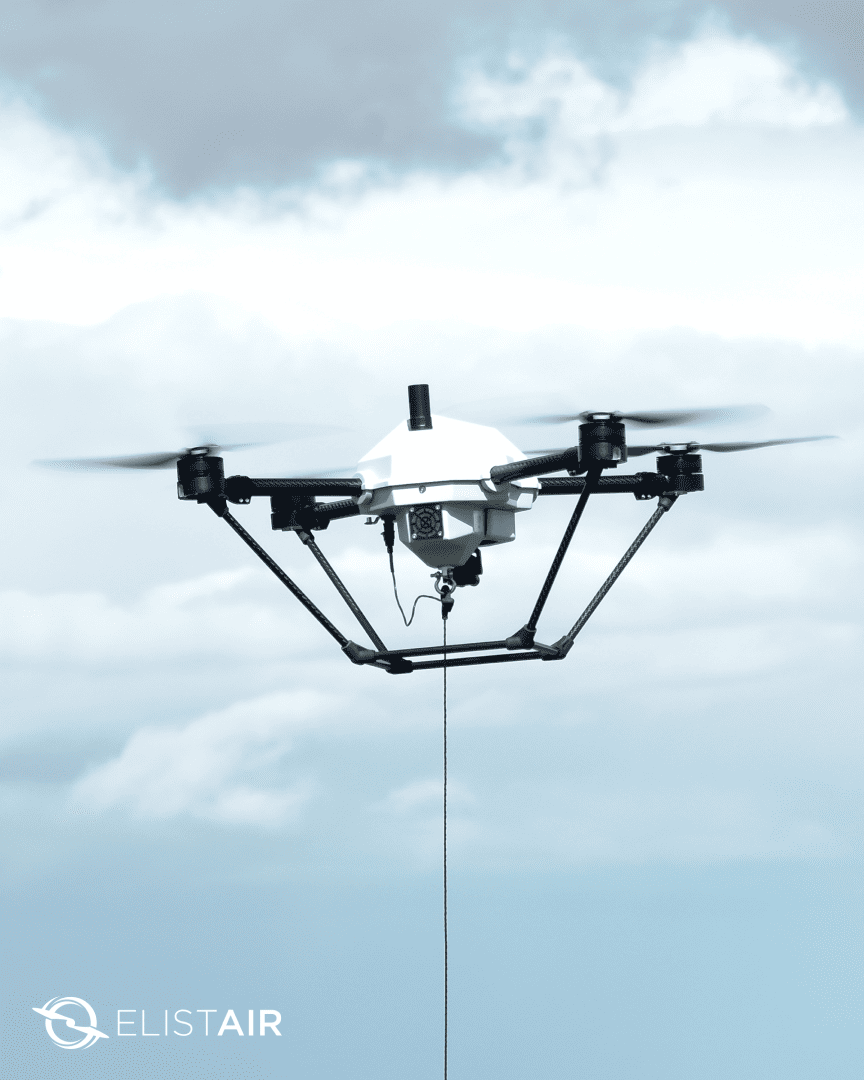
A tethered drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle physically connected to a ground station. More specifically, it consists of a base station/power station (tether station), drone tether, and the professional drone which is tethered to the station.
1- Tether station
Tethered drone stations can be operated from remote or rugged environment while performing numerous tasks. Their core functions are:
- Providing power
- Converting power
- Allowing communications between the UAV and the GCS (ground control station)
- Tether winch operations
2- Micro tether
Drone tethers connect the drone to a power station. They can be simply used for holding the drone in place or securing it’s hovering position. Top industry tethers comprise of conductors, fiber optic cables, and BPL dual lines suited for dual-comm links.
Tethered drones can be deployed for varied applications, though most focus on aerial observation and telecommunications.
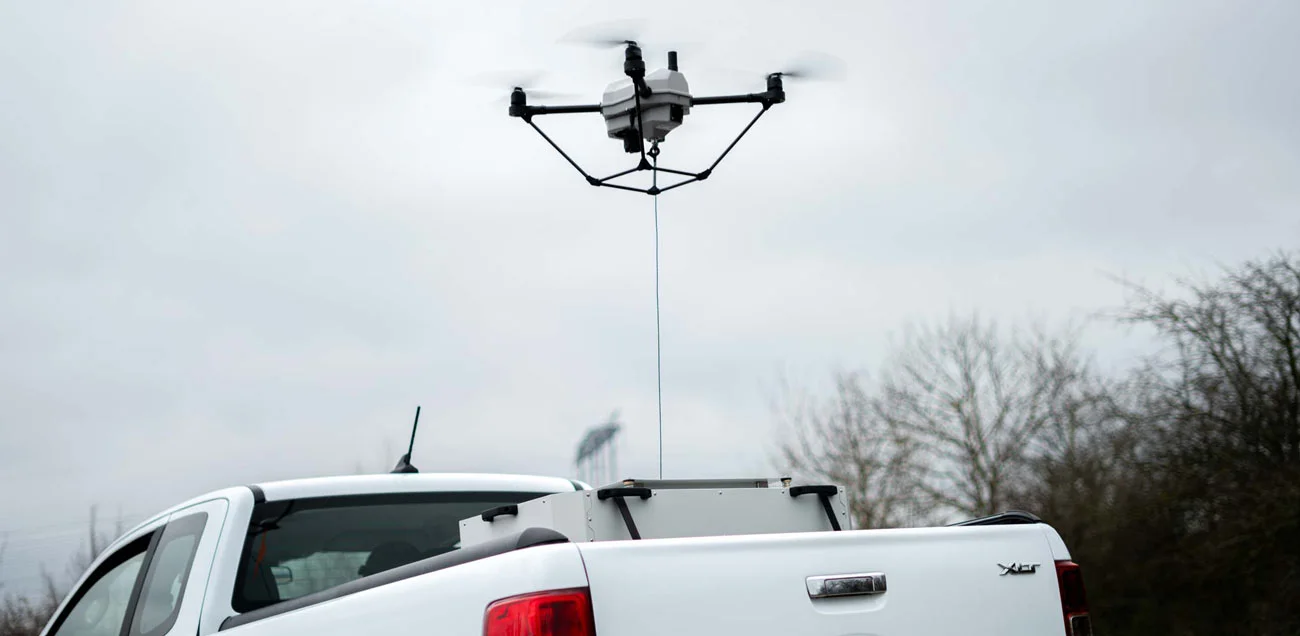

Uses of Tethered Drones
To grasp the applications of tethered UAVs, it’s essential to understand the constraints of drones that are not tethered.
The limitations of free-flying drone
- First limitation is flight time. With an average flight time of about 30 minutes, operators cannot keep flying the drone. They must land it, change the batteries, and then launch it again. The main benefit of a tether drone is its endurance of several hours.
- Safety is the second limitation: A predictable aerial presence is advantageous in evolving scenarios such as festivals, natural disasters, crowd surveillance, etc. However, despite their advanced technology, drones can still cause accidents. Tethered drones, on the other hand, eliminate the risk of the drone flying off and causing harm.
- The third limitation is ease of operation. While pilots need experience to safely deploy classic drones, tethered drones don’t require sophisticated drone piloting skills. With just a button press they climb to the requested altitude, and remain on station during the whole mission. Operators can then focus on their operation and benefit from a deeper situational awareness.
Tethered drones in the defense industry
Tethered drone technology is ideally suited for border security and Forward Operating Base (FOB) protection.
Military reconnaissance drones can be split into four categories:
- Micro drones, which have recon capabilities but are constrained by optical power and flight duration.
- Short-range reconnaissance drones are mainly used by squads and platoon-sized military regiments. They are used for determining the strength, location, and tactical weaknesses of the enemy – vital information for determining the right course of action.
- Mid-range reconnaissance drones are larger and carry more advanced payloads. They are known for their improved range and flight duration. Drones in this category are known for border security and FOB protection.
- Long-range reconnaissance drones. Small military drones run on LiPo batteries while the larger ones use aircraft fuel. The limitations posed by batteries and fuel are a limiting factor.

Border surveillance
Border security is complicated given the geographical expanse, natural terrain demarcations, the conflict-averse nature of disputed territory, and much more. When referring to border security, we are looking at all aspects of general security, surveillance at checkpoints, and monitoring of entry/exit points.
As an example, porous borders pose great natural security challenges to countries surrounded by hostile states as criminals and traffickers take advantage of the situation.
In parrallel, another concern is irregular or unchecked immigration – a task that requires a lot of investment in manpower to secure it. In brief, physical barriers like walls, trenches, and fences are only as good as the assets monitoring them.
FOB protection
Forward operating bases are complex to defend. They require in particular a great deal of manpower and assets to maintain an edge over the enemy should there be sporadic attacks. Also, infrastructural challenges are another factor affecting the ability of military bases to maintain communication at the FOB.
Mounted cameras can protect warfighters but cannot see as far as aerial cameras. Whereas Tethered drones provide aerial surveillance over a wide optical range. Especially with impressive zoom abilities, the cameras can detect vehicles and other large objects 10 km away.
Another upside to tethered drones is their endurance. Where guards are rotated in 8-10 hour shifts, tethered drones can fly long enough to overlap guard rotations.
Tactical communications
Areas manned by military personnel are vulnerable to attack and infiltration. Modern technological advancements expose vulnerabilities on unmanned aircraft to hacking.
The same applies to counter-UAS technologies, drone jamming technology, and infiltration equipment. Tethered drones are immune to a cyberattack or counter-UAS systems. The tether cable is a tactical communication link safeguarding the drone from infiltration.
Tethered drones for private and public safety
In addition to the defense sector, tethered drones are widely used for the securization of people and goods in the public and private areas. With their minor logisitcal footprint and their ability to cover wide areas at a glance they are a critical assets for security operators.
Indeed, a permanent eye in the sky with immediate video feedback provides a key situational awareness and considerably facilitates interventions. Examples of missions can be event surveillance, permiter securization or crowd monitoring to mention just a few.
First responders and emergency telecommunications
In emergencies, tethered drones provide a permanent view of hard-to-reach areas. They help responders see dangers and victims in real time. This allows for better coordination and a more effective response.
When equipped with communication tools, they can create temporary networks. These networks spread cellular, high-frequency radio, Wi-Fi, and 3G/4G signals over a wide area.

Benefits Of Tethered Drones
Autonomy – Tethered drones offer autonomous flight allowing the operators to focus on their mission more than on the piloting of the drone.
Flexible legislation – Legislation around tethered drones is flexible as several rules on commercial drones do not apply. In some countries, tethered drones are not seen as drones because they stay in one place while connected to the ground. In other countries, users of tethered drone systems are not mandated to have them registered as their free-flying counterparts. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) allows the use of these UAVs.
Limited spatial area – A tethered UAS operates within a limited spatial area restricted by the tether. This removes the risks of fly aways and crash on people or infrastructures.
Safe data transfer – While free-flying drones may occasionally lose their data links to interrupted flights or lost data links, tethered drones benefit from an uninterrupted yet secure line of communication between the ground station and the aircraft.
Dissuasion – Tethered drones are an overt deterrence mechanism. When operating a drone in public areas, safety is paramount. Tethered drones offer greater reliability than other market alternatives.
Auteur – Russel A